Mechanisms of DNA repair
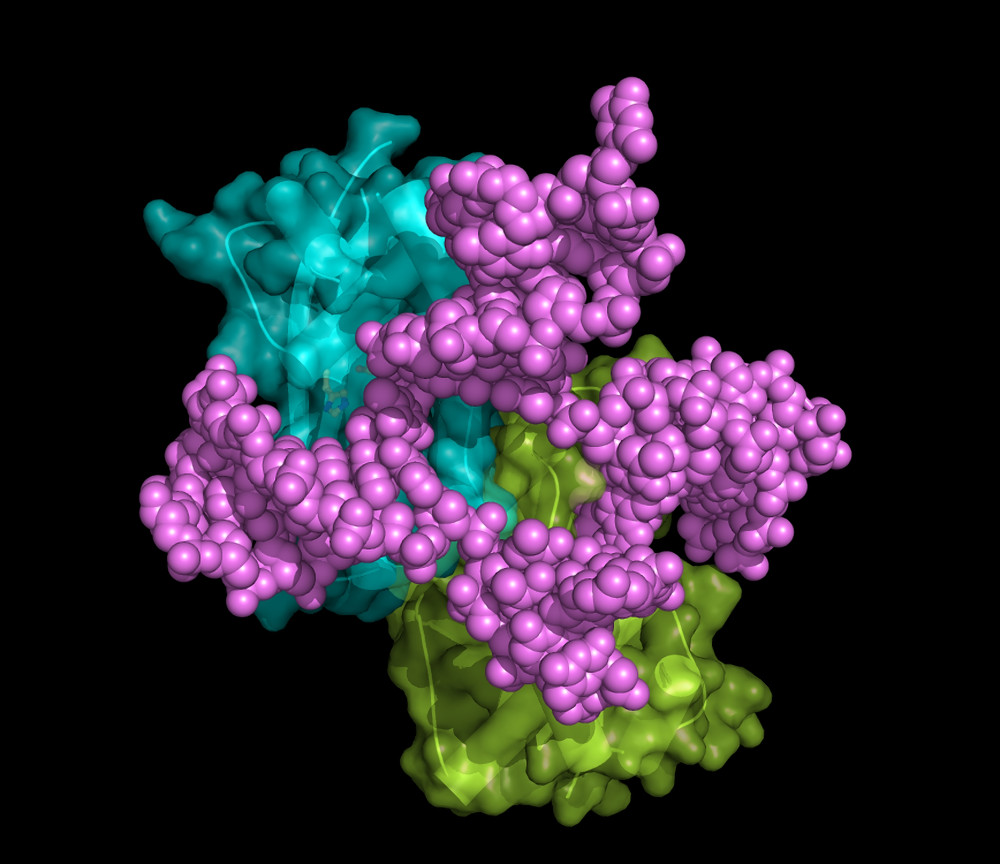 One of the projects at the International Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology in Warsaw studies the mechanisms of DNA repair, the role of which is to prevent the distortion of genetic information. The DNA molecule, which encodes information about how each cell and the whole organism are built and function, undergoes chemical damage, either spontaneously or under the influence of external factors (radiation, carcinogens etc.). Staff members of the Institute’s Laboratory of Protein Structure use protein crystallography, which allows them to determine the three-dimensional architecture of molecules and further elucidate their mechanism of action. The Laboratory has discovered, for example, the way the UvrA protein detects various DNA lesions and initiates repair. Another achievement involved elucidating the mechanism of the RuvC enzyme, which participates in a repair pathway in which a damaged region of DNA is fixed using a correct copy thereof. The team also determined the first structures of another important DNA repair enzyme – Slx1.
One of the projects at the International Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology in Warsaw studies the mechanisms of DNA repair, the role of which is to prevent the distortion of genetic information. The DNA molecule, which encodes information about how each cell and the whole organism are built and function, undergoes chemical damage, either spontaneously or under the influence of external factors (radiation, carcinogens etc.). Staff members of the Institute’s Laboratory of Protein Structure use protein crystallography, which allows them to determine the three-dimensional architecture of molecules and further elucidate their mechanism of action. The Laboratory has discovered, for example, the way the UvrA protein detects various DNA lesions and initiates repair. Another achievement involved elucidating the mechanism of the RuvC enzyme, which participates in a repair pathway in which a damaged region of DNA is fixed using a correct copy thereof. The team also determined the first structures of another important DNA repair enzyme – Slx1.
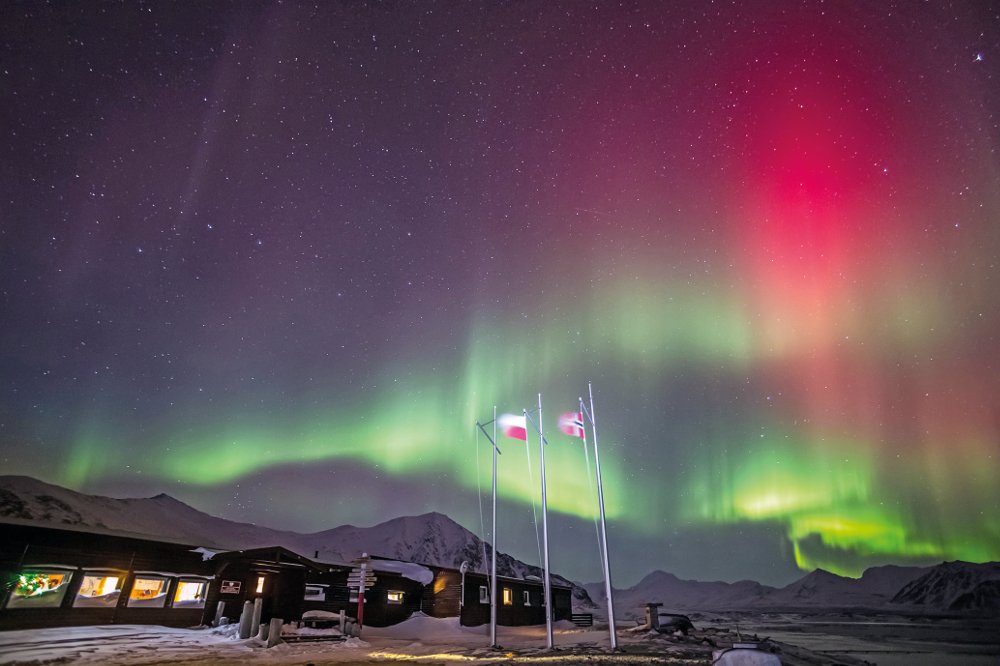
 Hornsund Polish Polar Station is situated on the bay of Isbjørnhamn in the fiord of Hornsund (in the southern portion of the Norwegian island of Spitsbergen, part of the Svalbard archipelago). Managed by the PAS Institute of Geophysics in Warsaw, the station conducts scientific research yearround and is proud to be Poland’s northernmost research institution. Together with Poland’s research vessels (including the “Oceania” research vessel of the PAS Institute of Oceanology), it forms the basis for the Polish Interdisciplinary Laboratory of Polar Research (PolarPOL). One of its objectives is to help identify the causes and effects of such global phenomena as climate change and to help counteract their negative consequences, through the sustainable use of water, natural resources, and preserving biological diversity.
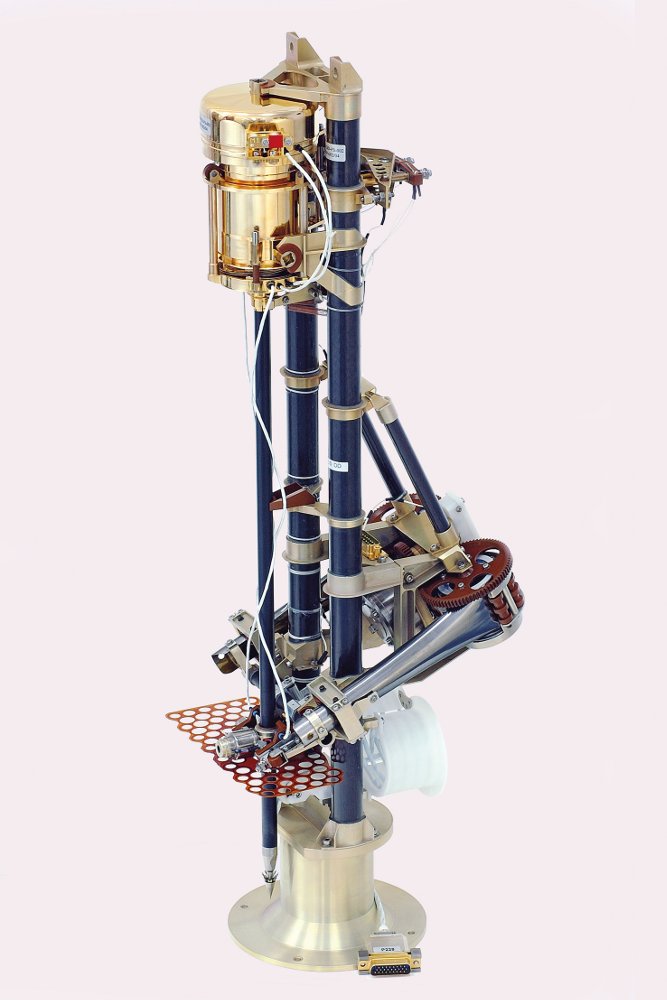
Hornsund Polish Polar Station is situated on the bay of Isbjørnhamn in the fiord of Hornsund (in the southern portion of the Norwegian island of Spitsbergen, part of the Svalbard archipelago). Managed by the PAS Institute of Geophysics in Warsaw, the station conducts scientific research yearround and is proud to be Poland’s northernmost research institution. Together with Poland’s research vessels (including the “Oceania” research vessel of the PAS Institute of Oceanology), it forms the basis for the Polish Interdisciplinary Laboratory of Polar Research (PolarPOL). One of its objectives is to help identify the causes and effects of such global phenomena as climate change and to help counteract their negative consequences, through the sustainable use of water, natural resources, and preserving biological diversity.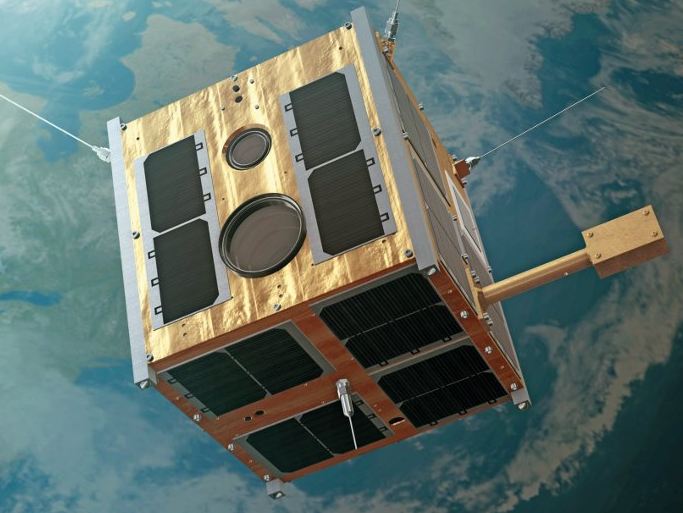 The PAS Space Research Center, Poland’s only unit dealing with human activity in space, developed and assembled the subcomponents of Lem and Heweliusz – the first Polish research satellites, which are now in Earth orbit. The satellites form part of the Bright Target Explorer (BRITE) international consortium, making precise measurements of the brightest stars in our galaxy.
The PAS Space Research Center, Poland’s only unit dealing with human activity in space, developed and assembled the subcomponents of Lem and Heweliusz – the first Polish research satellites, which are now in Earth orbit. The satellites form part of the Bright Target Explorer (BRITE) international consortium, making precise measurements of the brightest stars in our galaxy. The European Social Survey (ESS) is one of the largest and most important European research projects in the social sciences. In Poland it is carried out by the PAS Institute of Philosophy and Sociology. Under the EES project, a unique research method has been developed, making it possible to create maps illustrating shifts in social attitudes on key issues, the modification of value systems and human behavior. The survey provides a reliable source of information about the residents of the European Union. The data is available free-of-charge at
The European Social Survey (ESS) is one of the largest and most important European research projects in the social sciences. In Poland it is carried out by the PAS Institute of Philosophy and Sociology. Under the EES project, a unique research method has been developed, making it possible to create maps illustrating shifts in social attitudes on key issues, the modification of value systems and human behavior. The survey provides a reliable source of information about the residents of the European Union. The data is available free-of-charge at 

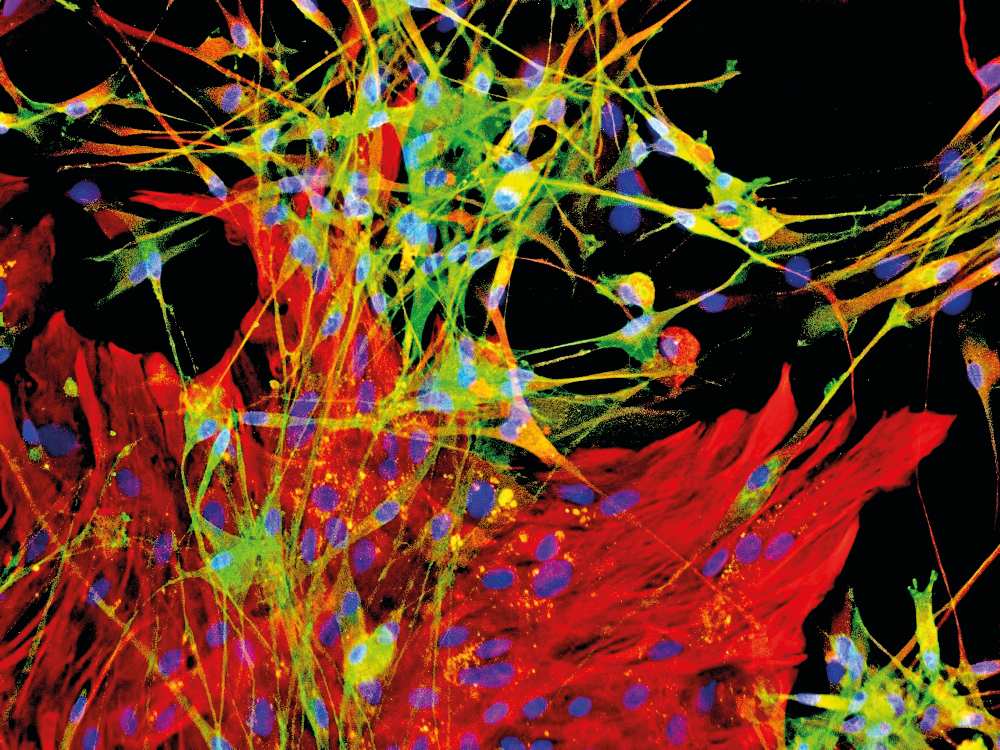 Specialists from the Hirszfeld Institute of Immunology and Experimental Therapy took part in an experiment in which severed nerve fibers and motor ability was restored for Dariusz Fidyka, a man whose spinal cord had been severed. The team took cells from the olfactory bulb, isolating specifically the olfactory ensheathing cells (OEC) together with fibroblasts. After 14 days in culture, the material was then transplanted by a team of specialists from the Neurosurgery Clinic at Wrocław Medical University. After six months of intensive exercise, the patient regained the ability to walk (using orthopedic parallel bars).
Specialists from the Hirszfeld Institute of Immunology and Experimental Therapy took part in an experiment in which severed nerve fibers and motor ability was restored for Dariusz Fidyka, a man whose spinal cord had been severed. The team took cells from the olfactory bulb, isolating specifically the olfactory ensheathing cells (OEC) together with fibroblasts. After 14 days in culture, the material was then transplanted by a team of specialists from the Neurosurgery Clinic at Wrocław Medical University. After six months of intensive exercise, the patient regained the ability to walk (using orthopedic parallel bars).